Broadening and narrowing search terms on Ovid databases - explode and focus
The terms ‘Explode’ and ‘Focus’, for example in the subject heading ‘Complimentary Therapies’, allows you to broaden or narrow your search.
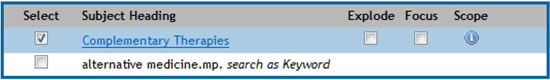
By selecting the ‘Explode’ option you will retrieve results that include the selected subject heading and all of the more specific terms that are listed below it in the ‘tree’. Terms in the tree that are preceeded by a ‘+’ sign have narrower terms indented below them. Click on the ‘+’ sign to expamd the list. ‘Explode’ will return more results - but more is not necessarily better. Only explode a term if the narrower terms are also relevant to you. If a search produces too many results, or if the results are not on topic, go back and look at any terms you exploded and check if all the narrower terms are relevant. Consider whether you should select one of these narrower terms rather than the broader one. You may need to use other methods like limits (which are discussed later) to narrow your results.
By selecting the ‘Focus’ option you will retrieve results in which the subject heading is considered one of the key concepts of the articles returned. ‘Focus’ will narrow the results, but can exclude some that are relevant as the subject heading may not be a key concept of the result. ‘Focus’ is particularly useful when a topic has been widely discussed in the literature and you need to quickly narrow your results to only those that discuss your concept in depth. If you have 'focussed' a term and your search contains too few results, go back and search again without ‘focussing’. ‘Focus’ and ‘explode’ can be used together.
You can complete your search without selecting either option, and you will retrieve results where the subject heading is a concept in the articles, including articles where it is one of the key concepts, but not include the more specific terms listed below it in the subject heading tree.
Subheadings
Many databases allow you to narrow your search by choosing specific subheadings. Although this is a useful option it is often best to keep the search as broad as possible initially. Evaluate the number and quality of your results, then narrow it later if necessary by using subheadings, limits, or combining more terms from your PICO question. Subheadings can help make your search more precise e.g. using the subheadings adverse effects, administration or dose for a drug, or using etiology or prognosis with a disease term.
Watch a video tutorial from the Cushing/Whitney Medical Library at Yale University that explains in depth about the advantages and options related to using subject headings in MeSH. [5]
Note: Our version of Ovid does not ‘auto explode’. You must choose ‘explode’ or ‘focus’ by ticking the appropriate box.
Playing time approximately 11 mins.
Activity 3: Searching using keywords or subject headings
Try searching using a keyword and compare this with a subject heading. This activity will help you understand the differences between these methods.
You might like to print this instruction page to refer to as you complete the activity.
- Open MEDLINE. You will see that the screen opens with “Advanced Search’ as the default in MEDLINE.
- Type dysphasia into the search box and untick the box ‘Map Term to Subject Heading’
- Click search
- There will be approximately 700 results. Review your results. How relevant are they?
- Now repeat the same search, but tick the box ‘Map Term to Subject Heading’
- Review the subject heading for dysphasia – it is called ‘Aphasia’ in the MEDLINE database
- Click on the subject heading ‘Aphasia’ to see the MeSH tree and all related terms in the thesaurus
- Click on the scope note icon to the far right of the term to learn more about the term aphasia
- Tick the subject heading ‘Aphasia’ and click ‘Continue’
- On the sub-headings screen tick ‘include all Subheadings’ and click ‘Continue’
- Scroll down to review your results. By choosing the subject heading term ‘Aphasia’ you now have approximately 4000 results, all of which will be associated with your topic of interest. By choosing only the keyword ‘dysphasia’ you would have missed articles that used alternative spellings or terminology for ‘dysphasia’.
